Learn Softmax Regression with PyTorch: A Colab-Based Demo
Objective: Use Softmax regression on the Fashion-MNIST dataset for 10-class classification, with a tool that lets you upload a local image, convert it to Fashion-MNIST style, and get the Top-3 predicted classes.
Key Point: Train with CrossEntropyLoss (built-in LogSoftmax + NLLLoss), and only run softmax when you need probability outputs.
Device: Fixed to CPU
1. Environment Setup & Dependencies for PyTorch (CPU Mode)
Import PyTorch/TorchVision and fix execution to CPU.
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
# Force CPU
device = torch.device('cpu')
2. Data Loading & Preprocessing for Fashion-MNIST in PyTorch
Download the Fashion-MNIST dataset, normalize pixel values to the range [0, 1], and create batched data loaders for efficient iteration.
Note: In notebook environments, use num_workers=0 to prevent multiprocessing shutdown warnings.
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
train_ds = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
test_ds = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
batch_size = 256
train_iter = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=0, pin_memory=False)
test_iter = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=0, pin_memory=False)
len(train_ds), len(test_ds)
3. Class Names (Aligned with Dataset Encoding)
Use the dataset’s built‑in classes to avoid mismatches from manual ordering.
classes = train_ds.classes
classes
4. PyTorch Softmax Regression Model Definition (Flatten + Linear Layer)
Flatten + Linear(784→10), outputs raw logits only (Softmax will be applied later by the loss function).
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(), # 28x28 -> 784
nn.Linear(784, 10) # Linear classifier (multiclass logistic regression)
).to(device)
def init_weights(m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
net.apply(init_weights);
net
5. Loss Function & Optimizer
Specify the training objective and update rule for the parameters.
Note: CrossEntropyLoss = LogSoftmax + NLLLoss (stable).
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
6. Evaluation Function
@torch.no_grad()
def evaluate(model, data_iter):
model.eval()
correct, total = 0, 0
for X, y in data_iter:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
logits = model(X)
pred = logits.argmax(dim=1)
correct += (pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.numel()
return correct / total
7. Training Loop in PyTorch with CrossEntropyLoss
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
num_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
net.train()
running_loss, running_acc, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
for X, y in tqdm(train_iter, leave=False):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
logits = net(X) # Forward: logits (no softmax)
loss = loss_fn(logits, y) # Internally: LogSoftmax + NLLLoss
trainer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
trainer.step()
bs = y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item() * bs
running_acc += (logits.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
n += bs
train_loss = running_loss / n
train_acc = running_acc / n
test_acc = evaluate(net, test_iter)
print(f"epoch {epoch:02d} | train_loss={train_loss:.4f} | train_acc={train_acc:.4f} | test_acc={test_acc:.4f}")
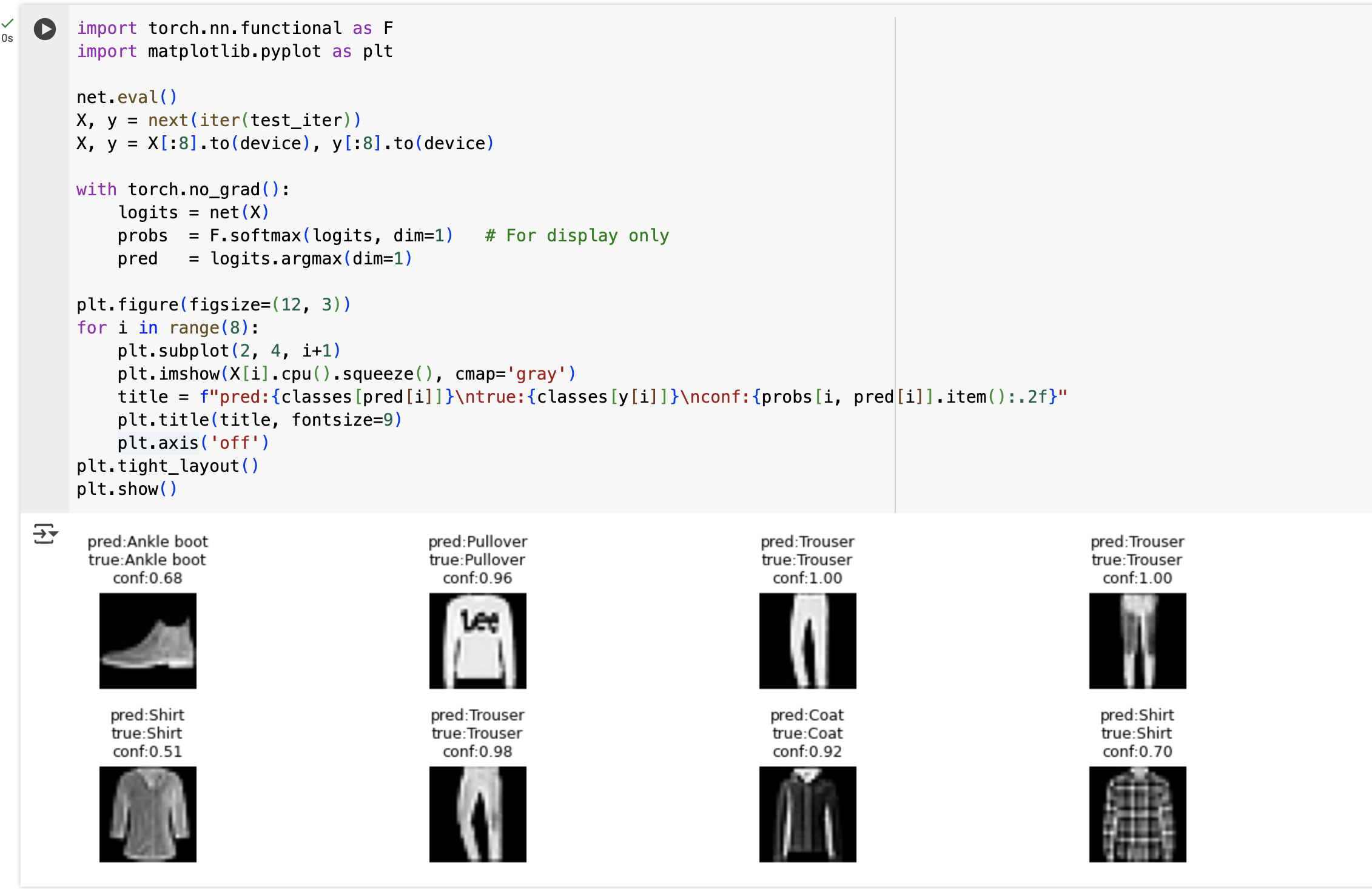
8. Inference & Visualization: Softmax Probabilities in PyTorch
Take a random batch and show predictions / true labels / confidence.
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
net.eval()
X, y = next(iter(test_iter))
X, y = X[:8].to(device), y[:8].to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
logits = net(X)
probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=1) # For display only
pred = logits.argmax(dim=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
for i in range(8):
plt.subplot(2, 4, i+1)
plt.imshow(X[i].cpu().squeeze(), cmap='gray')
title = f"pred:{classes[pred[i]]}\ntrue:{classes[y[i]]}\nconf:{probs[i, pred[i]].item():.2f}"
plt.title(title, fontsize=9)
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
9. A Test
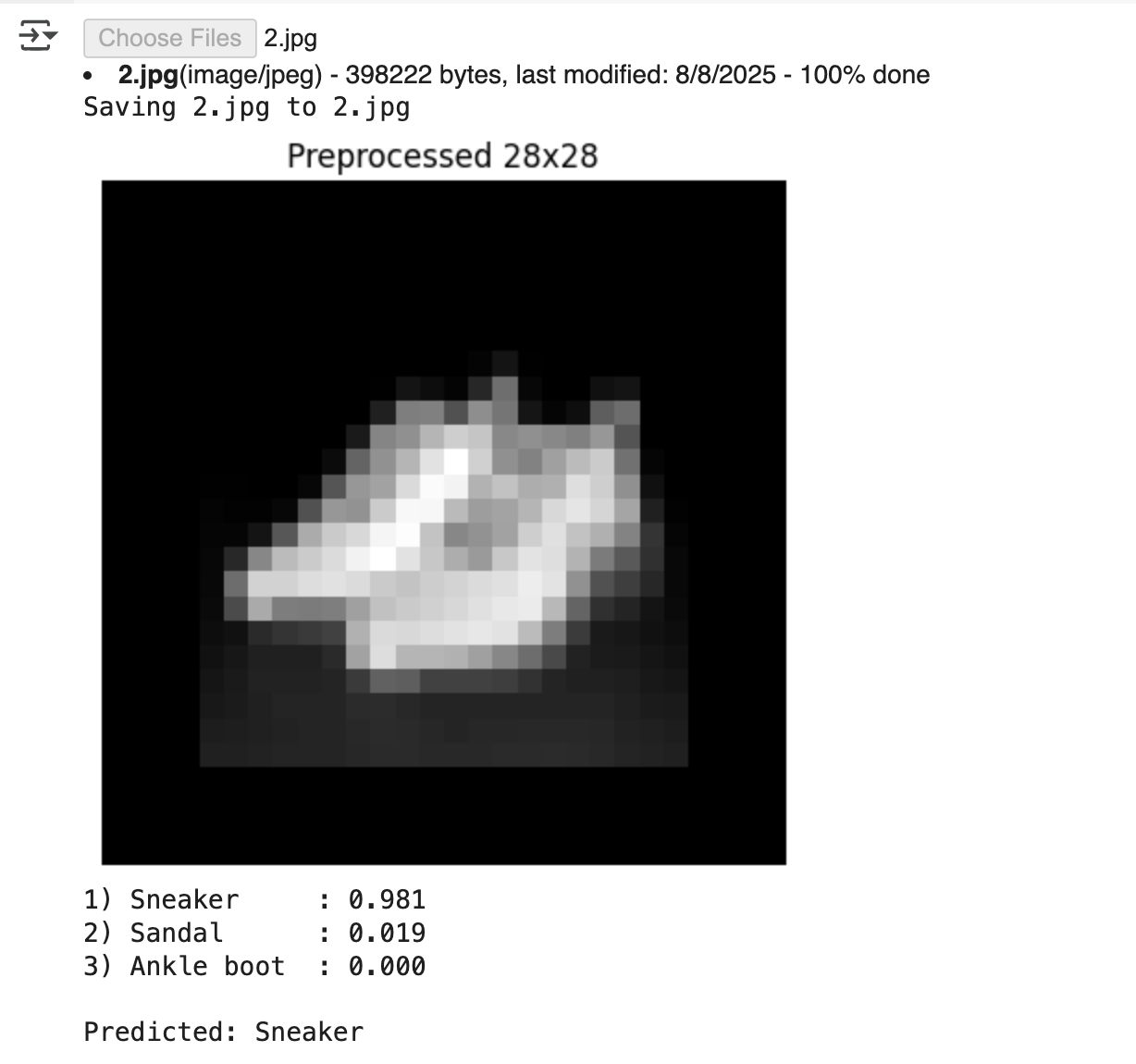
Upload an image, process it into FMNIST style, and output the Top-3 predicted classes with their confidence scores.
from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageStat
import numpy as np
import torch
from google.colab import files
# === Upload ===
uploaded = files.upload()
img_path = list(uploaded.keys())[0]
# === Preprocess: Make the real image resemble FMNIST style ===
def preprocess_to_fmnist(path):
img = Image.open(path).convert('L') # Grayscale
# Invert if background is bright
mean_val = ImageStat.Stat(img).mean[0] / 255.0
if mean_val > 0.5:
img = ImageOps.invert(img)
# Auto-contrast
img = ImageOps.autocontrast(img)
# Resize with aspect ratio preserved: longest side = 20px, center on 28×28 black background
max_side = 20
w, h = img.size
scale = max_side / max(w, h)
new_w, new_h = max(1, int(w * scale)), max(1, int(h * scale))
img_small = img.resize((new_w, new_h), resample=Image.BILINEAR)
canvas = Image.new('L', (28, 28), 0)
left = (28 - new_w) // 2
top = (28 - new_h) // 2
canvas.paste(img_small, (left, top))
# Convert to tensor and normalize using FMNIST stats
x = torch.from_numpy(np.array(canvas)).float() / 255.0
mean, std = 0.2860, 0.3530
x = (x - mean) / std
x = x.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # [1,1,28,28]
return canvas, x
canvas, x = preprocess_to_fmnist(img_path)
# Show the preprocessed 28x28 image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(canvas, cmap='gray'); plt.axis('off'); plt.title('Preprocessed 28x28'); plt.show()
# === Inference Top‑3 ===
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
logits = net(x.to('cpu'))
probs = torch.softmax(logits, dim=1).squeeze(0)
# Use dataset-provided class names
classes = train_ds.classes
top3 = torch.topk(probs, k=3)
for i in range(3):
cls_idx = top3.indices[i].item()
print(f"{i+1}) {classes[cls_idx]:12s}: {top3.values[i].item():.3f}")
print("\nPredicted:", classes[top3.indices[0].item()])
Quick Notes
-
Where is Softmax? Answer: It’s handled internally by
CrossEntropyLossduring training. Only apply softmax explicitly when you need to output probabilities. -
Why is it stable? Answer: It leverages the
log-sum-exptrick to prevent numerical overflow. -
For real-world images Answer: Preprocess them to resemble
FMNISTsamples. For better accuracy, consider replacing the model with a small CNN — even two convolutional layers can push accuracy above 90%. Here, we’re only using it as aSoftmaxdemo.